

However, the key finding is that Sarah's score was not one of the best marks. Hence, 24.86% of the scores (0.2486 x 100 = 24.86%) were lower than Sarah's, but above the mean score. We can also see how well she performed relative to the mean score by subtracting her score from the mean (0.5 - 0.2514 = 0.2486). Going back to our question, "How well did Sarah perform in her English Literature coursework compared to the other 50 students?", clearly we can see that Sarah did better than a large proportion of students, with 74.86% of the class scoring lower than her (100% - 25.14% = 74.86%). In other words, around 25% of the class got a better mark than Sarah (roughly 13 students since there is no such thing as part of a student!).
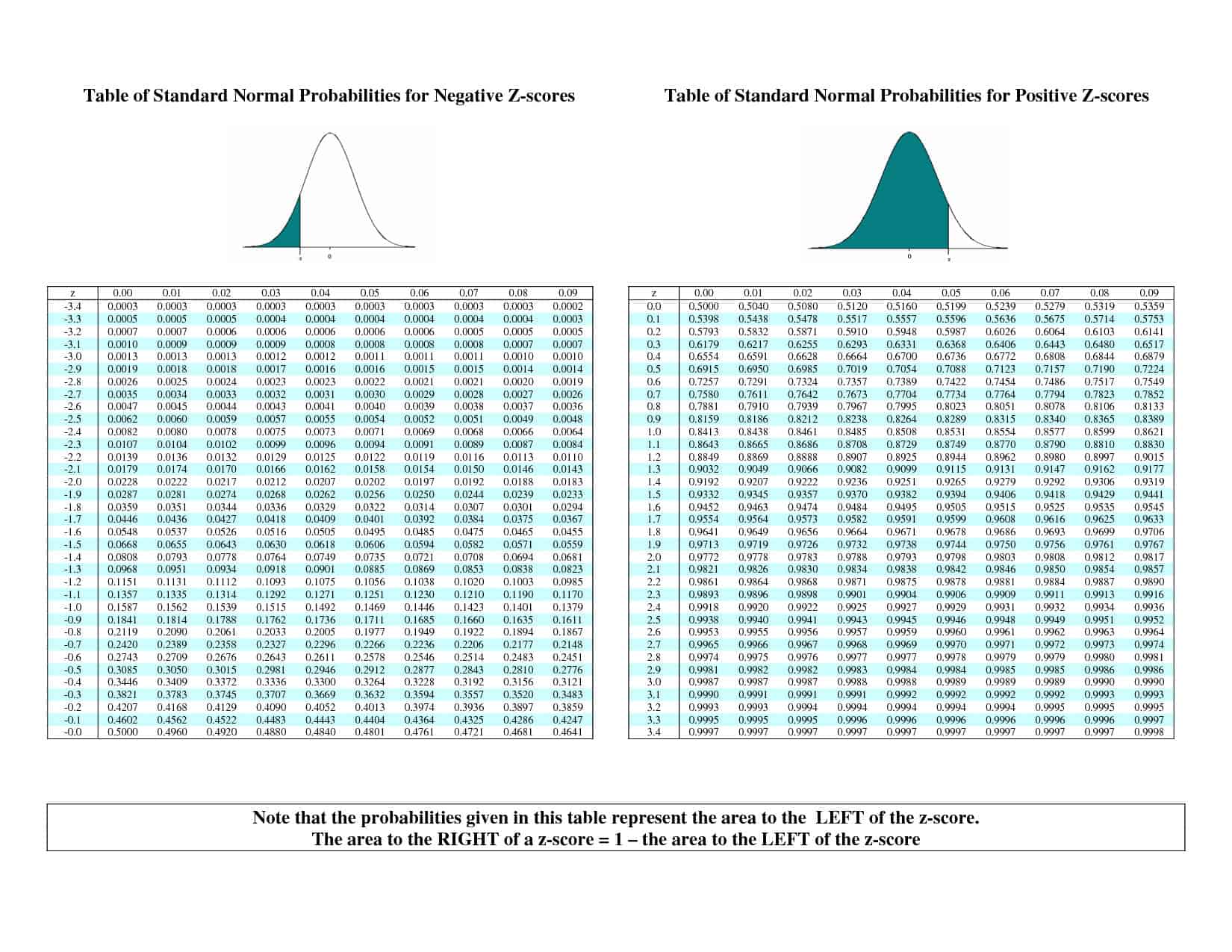
If we look at this as a percentage, we simply times the score by 100 hence 0.2514 x 100 = 25.14%. This means that the probability of a score being greater than 0.67 is 0.2514. Therefore, we start with the y-axis, finding 0.6, and then move along the x-axis until we find 0.07, before finally reading off the appropriate number in this case, 0.2514. Example: Standard deviation in a normal distribution You administer a memory recall test to a group of students. Z-scores are particularly useful to monitor changes in patients with a BMI above the 99th percentile. The y-axis in the table highlights the first two digits of our z-score and the x-axis the second decimal place. This tool allows you to calculate the body mass index (BMI) of your patients between the ages of 2 and 20 years, as well as the exact BMI percentile and z-score (standard deviation), based on the Center for Disease Control (CDC) growth charts. When you calculate a z-score you are converting a raw data value to a standardized score on a standardized normal distribution. You can calculate a z-score for any raw data value on a normal distribution. To use the table, which is easier than it might look at first sight, we start with our z-score, 0.67 (if our z-score had more than two decimal places, for example, ours was 0.6667, we would round it up or down accordingly hence, 0.6667 would become 0.67). The z-score is the number of standard deviations a data point is from the population mean. This table helps us to identify the probability that a score is greater or less than our z-score score.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
